Traffic turns off Broadway in Upper Manhattan, Feb. 23, 2022. Ben Fractenberg/THE CITY
 This article was originally published by The CITY on Feb. 25
This article was originally published by The CITY on Feb. 25
It could be doom for the vroom.
That’s what officials and light sleepers are hoping for when a state law aimed at deterring noisy, souped-up vehicles goes into effect this spring, coupled with an ongoing pilot program by the city to automatically detect and ticket loud roadsters.
The goal is to address ear-splitting clamor from cars and motorcycles amid a rising volume of complaints. The revving of engines, popping of tailpipes and blaring of speakers add to the cacophony of urban life and can pose health threats to New Yorkers.
Exposure to noise can cause hearing loss, exacerbate stress and disrupt sleep, experts say.
“Short of it affecting blood pressure, cardiovascular disorders, it diminishes quality of life,” said Arline Bronzaft, professor emerita of Lehman College and a longtime researcher on the effects of loud sounds on our psyches.
Many New York City residents welcome the enforcement, while some car and motorcycle enthusiasts think the efforts are misguided.
Ricardo Picon, a photographer and former musician who lives with his wife in Bushwick, said the noise from modified cars has interrupted his sleep and made his home tremble, especially in the warmer months.
“I come from being a night person and dealing with sound and dealing with noise. This is how crazy it is. It got to the point where it became a nightmare,” he said. “You don’t need to measure the decibels to hear how it rumbles two or three blocks… This has become an epidemic in the boroughs.”
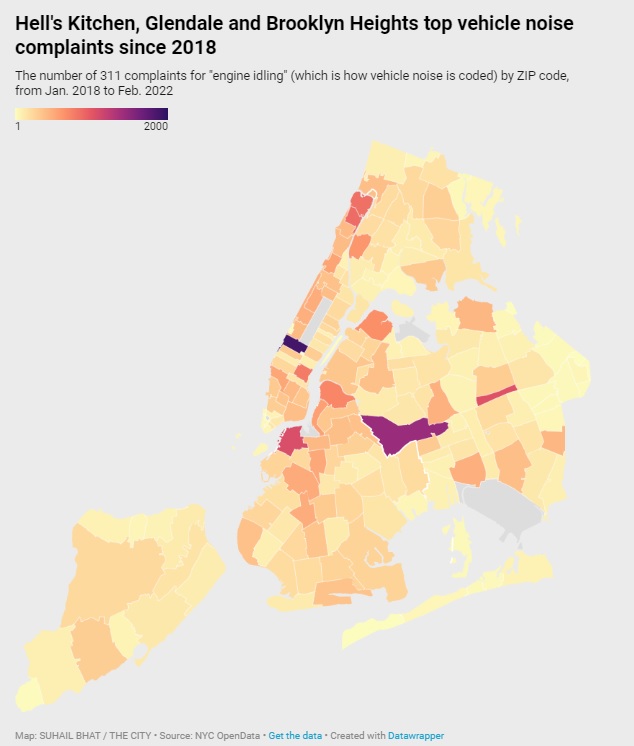
Noise complaints, specifically for loud vehicles, rise and fall seasonally, and they’ve been on the upswing since the pandemic began. Glendale, Queens, which shares a border with Picon’s neighborhood, saw the second-highest number of complaints of loud vehicles per zip code, right after Hell’s Kitchen in Manhattan, since 2018.
‘Obnoxious and Antisocial Behavior’
Gov. Kathy Hochul signed the Stop Loud and Excessive Exhaust Pollution Act into law in October and it will take effect in April.
The SLEEP Act raises fines from $150 to $1,000 for any illegal modifications of mufflers and exhaust systems that allow cars and motorcycles to become noisier.
The law applies to not only vehicle owners who seek the modifications, but the repair shops that make them or sell relevant parts. The shops can stand to lose their operating license or certificate to inspect vehicles if they’re caught three times within 18 months.
The aim is to “crack down on the supply issue and really stop these mufflers from being installed in the first place,” said Sen. Andrew Gounardes (D-Brooklyn), who sponsored the bill.
“It’s incredibly obnoxious and antisocial behavior to put a jet engine on the back of a souped-up Mazda and ride down Third Avenue on a Wednesday morning at 10 o’clock.”
The City
Anthony Pennachio, the president of both the motorcycle riding club Bikers of Brooklyn and car club Drivers of Brooklyn, is against programs to lower the volume. He said modified exhaust systems are common on the vehicles of people he knows.
“I would hope that the New York City police officers are smart enough to realize that that’s not something they should be giving a ticket for,” he told THE CITY. “Amplified volume is imperative to keep us safe” when riding motorcycles.
Bikers have argued for decades that the noise they make helps cars, trucks and even pedestrians know they’re around and avoid accidents.
But Pennachio conceded he has modified four of the 11 cars he owns to enhance the rumbling of the engine, as a matter of pleasure, not safety.
“Just to know you’re in a beefier man’s car,” he said.
On the other hand, Pennachio doesn’t understand why some mufflers are changed to make a gunfire-like sound, which “makes me jump out of my skin,” he said.
Hearing Loss
The SLEEP Act enforces the decibel limits set by the state’s Vehicle and Traffic law, which, caps the sound between 76 and 90 decibels, depending on speed and vehicle type.
On top of that, the city’s noise code specifies that cars of 10,000 pounds or less aren’t allowed to make sounds that a person can hear from more than 150 feet away. For heavier vehicles and motorcycles the distance is 200 feet.
But the law doesn’t doesn’t compel law enforcement to issue tickets, nor does it require police cars to be equipped with decibel readers.
“You have to be caught driving this way, drag racing on a highway or something and be caught by a police car, which is an imperfect system for sure,” Gounardes said.
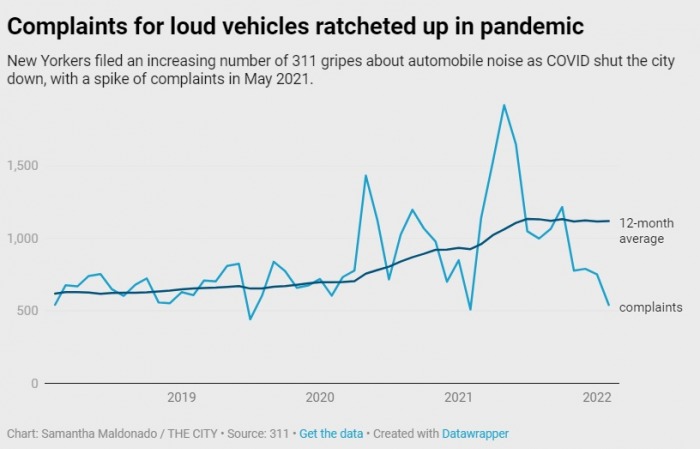
In 2021, New Yorkers filed the most complaints about engine idling since 2018: 13,489 complaints. The police issued 75 summons in response to complaints, data shows.
Specifically, police issued 14 summonses for excessive vehicle noise — the most between 2018 and the present, a period in which the police issued a total of 26 excessive vehicle noise summonses.
“When an officer conducts a car stop, there’s a possibility they can issue more than one summons and various types of summonses,” said Jessica McRorie, an NYPD spokesperson.
Gounardes called “automated enforcement” the “ultimate answer” to solving the excessive noise problems, and to that end, is sponsoring a bill that would create a noise camera pilot program in New York City modeled after the existing speed camera program.
Robo-Noise-Cop
The city, through the Department of Environmental Protection, is already testing that idea through a pilot program that quietly started in July and will run through June, at which point it may be ended or expanded.
A sound meter records vehicles passing by. If it captures a sound at least 50 feet away that is above 85 decibels — for reference, that’s around the sound of a blender or a lawn mower — a camera records images of the vehicle’s license plate.
After DEP’s noise enforcement staff reviews the video, the DEP sends a notice to the registered owner of the vehicle, who will then have to show up for an inspection.
Neither the pilot nor the SLEEP Act are intended to be a check on cars that blast music.
The camera-sound meter combo is placed in just one location in the city, according to DEP spokesperson Ted Timbers, who declined to specify where.
“This technology offers some real promise in helping us to provide some relief for our neighbors,” DEP Commissioner Rit Aggarwala said in a statement.

A tow truck barrels up University Avenue in The Bronx, Feb. 23, 2022. Ben Fractenberg/THE CITY
So far, the DEP has issued 71 notices to appear based on the new gadget.
But the inspections may end this spring, with DEP issuing violations based on the evidence from the sound meter.
Vehicle owners found to be in violation may be fined $220 for a first offense.
And as a result of the SLEEP Act, fines doled out for vehicle noise violations in New York City will increase this spring, to $800 for a first violation.
The DEP says it won’t share the data the cameras collect with other agencies, like the NYPD. And the cameras in theory eliminate any subjective enforcement. But still, there are concerns.
“In one sense, we would prefer to have police involvement as little as possible,” said Jerome Greco, digital forensics supervising attorney at the Legal Aid Society. “At the same time, automated systems are not a complete solution and are not infallible — my concern being they’ll use this in some automated way to fine people and put the burden on them to prove it wasn’t them or they didnt do anything wrong.”
Chris Olivere, owner of the Brooklyn-based car customization shop Modified Workz, pointed out that even new cars can “come naturally loud,” like a Lamborghini or Mercedes-Benz.
Several years ago, Olivere, now 31, got a summons for excessive noise coming from his “brand new” Mazda. He fought the ticket and it was thrown out.
“It’s a way to waste your time, honestly,” he said.
THE CITY is an independent, nonprofit news outlet dedicated to hard-hitting reporting that serves the people of New York.